需要が高まってきているバイノーラル処理にチャレンジする場合、まずはWeb上のSOFA形式のHRTFデータで試すことが多いかと思います。
Pythonであれば、SOFA形式のデータ読み込んで Numpy配列にさえ変換すればバイノーラル処理やプロットは容易です。
そこで、今回はPythonでSOFA形式のデータを扱う方法をサンプルコードとともに紹介します。
SOFA 形式について
VRや360°映像における、3次元音響(イマーシブ・オーディオ)を忠実に再現するには、頭部伝達関数(HRTF)やBRIRなどの音響データが不可欠です。
このような音響データは音源の方向や距離,受聴者などの大量に条件ごとに測定をする必要があります。また、測定した室内や機器などの情報もイマーシブ・オーディオのレンダラーには重要な情報となっています。
この音響データとメタ情報を共有しやすいように共通のフォーマットとして定義しているのが SOFA (Spatially Oriented Format for Acoustics) になります。
詳しくは、以下のWebサイトをご覧ください。
General information on SOFA - Sofaconventions
SOFAを処理するためのPython用API
SOFA を処理するための各言語向け API が公開されています。
Software and APIs - Sofaconventions
特にPythonでは、以下のようなAPI(モジュール)があります*1。
著者はFIR型データの読み込み用途で pysofaconventions と python-sofa を少しだけ利用したことがあります。
前者はサンプルコードがあるので取っつき易く、とりあえず音響データをNumpy配列として引っ張ってくるだけなら簡単に扱える印象です。ただし、
後者はAPIのドキュメントが用意されておりSOFA形式について知識があれば扱いやすい気がしましたが、サンプルコードが少ないです。
そこで、今回はpysofaconventionsで適当なHRTFデータベースのデータを読み込んでみます。
pysofaconventions を使ってみる
インストール方法
githubに書いてあるように、pipで導入できます。
pip install pysofaconventions
利用するデータベース
以下のWebサイトでは、様々な公開SOFAデータへのリンクがあります。
Files - Sofaconventions https://sound.media.mit.edu/resources/KEMAR/hrtfdoc.txt
今回はこの中から、有名な KEMARダミー ヘッドを使ったMITのデータ(MIT-KEMAR)のmit_kemar_normal_pinna.sofaを利用します。
サンプルコードについて
以下のサンプルコードを改造し、解説用にしました。
pysofaconventions/plotListenHRTF.py at master · andresperezlopez/pysofaconventions · GitHub
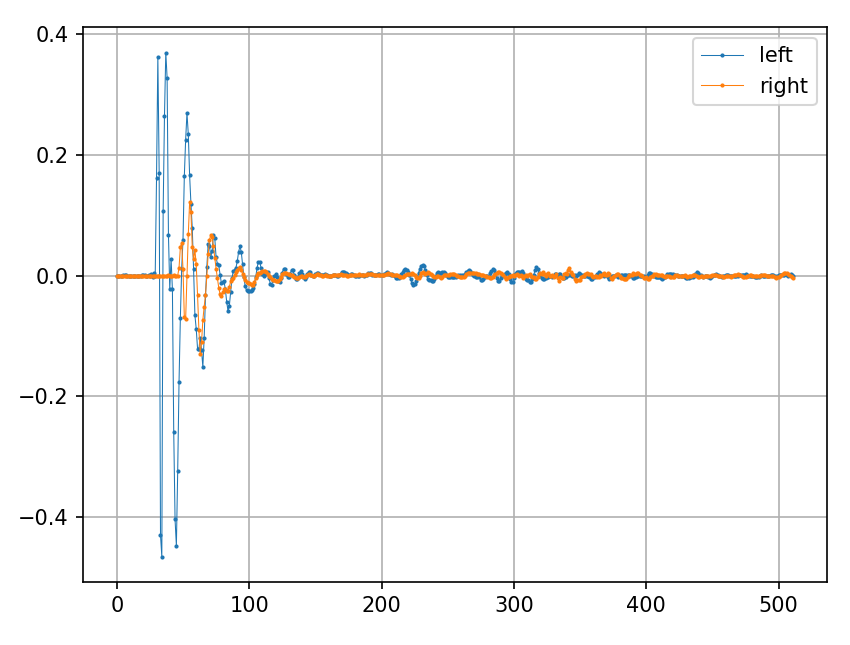
コードの前半では HRTF のインパルス応答となる HRIRを抽出しています。
hrir_allは (音源位置,2,IR長)の3次元配列であり、特定の音源位置から到来する音をシュミレーションするために 方位角60度,仰角30度位置のデータを抽出した2次元配列のhrirを作成しています。
後半では、hrirを任意のモノラル信号に畳み込むことでバイノーラル化しています。
import numpy as np import pysofaconventions import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import scipy.signal import soundfile as sf # SOFA形式ファイルを読み込む sofa_filepath = 'mit_kemar_normal_pinna.sofa' # SOFAFileオブジェクトとして読み込まれる sofa = pysofaconventions.SOFAFile(sofa_filepath, 'r') # 各オブジェクトの次元(数)に関する情報を標準出力 # - I : 1 # - C : 3 # - Number of receivers (R) : 2 (測定マイク位置。両耳なので2) # - Number of emitters (E) : 1 (音源位置の数) # - Number of data samples (N) : 512 (HRTFの長さ(サンプル)) # - Number of measurements (M) : 710 (測定位置の数) # - S : 0 # (ある場合は)信号源 print("Dimensions:") sofa.printSOFADimensions() print("\n") # 変数 print("Variables") sofa.printSOFAVariables() # ListenerPosition = (1, 3) 聴取者の位置 # ReceiverPosition = (2, 3, 1) マイクロホン位置 # SourcePosition = (710, 3) 音源位置 # EmitterPosition = (1, 3, 1) 音源位置 # ListenerUp = (1, 3) 聴取者の頭の高さ # ListenerView = (1, 3) 聴取者の向き # Data.IR = (710, 2, 512) IRデータのnumpy配列のshape # Data.SamplingRate = (1,) サンプリング周波数 # Data.Delay = (1, 2) 遅延 print("\n") # サンプリング周波数を確認 samplerate_sofa = sofa.getVariableValue('Data.SamplingRate') print(f"samplerate_sofa: {samplerate_sofa}\n") # samplerate_sofa: [44100.] # 測定した音源位置の一覧を取得。 print("Source Positions") sourcePositions = sofa.getVariableValue('SourcePosition') # 2次元配列(masked_array)で、音源位置ごとの方位角・仰俯角・距離情報を表している print(sofa.getPositionVariableInfo('SourcePosition')) print(sourcePositions) # 例:方位角が 0 (正面)のインデックスとデータを抽出 center_indices = np.where(sourcePositions[:,0]==0) print(center_indices) print(sourcePositions[center_indices]) print("\n") """ >>> print(center_indices) (array([ 0, 56, 116, 188, 260, 332, 404, 476, 536, 592, 637, 673, 697, 709], dtype=int64),) >>> print(sourcePositions[center_indices]) [[ 0. -40. 1.4] [ 0. -30. 1.4] [ 0. -20. 1.4] [ 0. -10. 1.4] [ 0. 0. 1.4] [ 0. 10. 1.4] [ 0. 20. 1.4] [ 0. 30. 1.4] [ 0. 40. 1.4] [ 0. 50. 1.4] [ 0. 60. 1.4] [ 0. 70. 1.4] [ 0. 80. 1.4] [ 0. 90. 1.4]] """ # HRIR (インパルス応答)を抽出 hrir_all = sofa.getDataIR().data #masked_arrayなので、dataを抜き出す print(hrir_all.shape) print("\n") # (710, 2, 512) # 方位角60度,仰角30度のIRデータを抜き出す index = np.where(np.logical_and(sourcePositions[:,0]==60, sourcePositions[:,1] == 30, sourcePositions[:,2] == 1.4))[0] print(index) print(sourcePositions[index].data[0]) # array([486], dtype=int64) # array([ 60. , 30. , 1.4]) hrir = np.squeeze(hrir_all[index]) print(hrir.shape) # (2, 512) # プロット plt.plot(hrir[0], label="left", linewidth=0.5, marker='o', markersize=1) plt.plot(hrir[1], label="right", linewidth=0.5, marker='o', markersize=1) plt.grid() plt.legend() plt.show() # モノラル信号にHRIRを畳みこむ。 audio_filepath = "chirp.wav" x_mono, samplerate_x = sf.read(audio_filepath) if samplerate_x != samplerate_sofa: print("Error: samplerate mismatch") exit(1) # Convolve it with the hrir x_binaural_left = scipy.signal.fftconvolve(x_mono, hrir[0]) x_binaural_right = scipy.signal.fftconvolve(x_mono, hrir[1]) x_binaural = np.asarray([x_binaural_left, x_binaural_right]).swapaxes(-1,0) # save sf.write('binaural.wav', x_binaural, samplerate_x)
関連リンク
- SOFA (Spatially Oriented Format for Acoustics) - Sofaconventions
- Two!Ears documentation — The Two!Ears Auditory Model <unknown> documentation
- バイノーラル再生とSOFAがもたらす未来 - MUSIC EcoSystems | BIZ
- 頭部伝達関数による音像定位 ——個人化へ向けたデータ群と課題—— 岩谷幸雄
- AES Standard » AES69-2022: AES standard for file exchange - Spatial acoustic data file format
*1:2023年4月現在,著者が見つけられたもののみ掲載